Class 9 Physics Chapter 6 numerical problems are according to the new syllabus of the Punjab Board. Chapter 6 is related to Mechanical Properties of Matter in which you will study the work, power, energy, types of energy, and efficiency of matter.
Class 9 Physics Chapter 6 Numerical Problems
The problems have been solved with easy-to-use methods using the following formulae:
F = kx
ρ = m/V
P = F/A = mg/A
ρ₁gh₁ = ρ₂gh₂
P = ρgh
Numerical Problems Chapter 6 – Mechanical Properties of Matter
6.1. A spring is stretched 20 mm by a load of 40 N. Calculate the value of spring constant. If an object cause an extension of 16 mm, what will be its weight?
Solution:
Force (F₁) = 40 N
Extension (x₁) = 20 mm = 20/1000 m = 0.02 m
Extension (x₂) = 16 mm = 16/1000 m = 0.016 m
Spring Constant (k) = ?
Weight (w = F₂) = ?
Let’s use Hooke’s Law
F = kx
Step 1: Find spring constant k
k = F₁/x₁
k = 40/0.02
k = 2000 N/m
k = 2×1000 N/m
k = 2 kN/m
Step 2: Find weight for 16 mm extension
Using F = kx
F₂ = k × x₂
F₂ = 2000 × 0.016
F₂ = 32 N
6.2. The mass of 5 litres of milk is 4.5 kg. Find its density in SI units
Solution:
Volume (V) = 5 L = 5 × 10⁻³ m³
Mass (m) = 4.5 kg
Density (ρ) = ?
Use density formula
ρ = m/V
ρ = 4.5/(5 × 10⁻³)
ρ = 900 kg/m³
ρ = 0.9 × 10³ kg/m³
6.3. When a solid of mass 60 g is lowered into a measuring cylinder, the level of water rises from 40 cm³ to 44 cm³. Calculate the density of the solid.
Solution:
Initial volume (V1) = 40cm3
Initial volume (V2) = 44cm3
Volume displaced = Final volume- Initial volume
V = V2 – V1
V = 44 – 40
V = 4 cm³
V = 4 × 10⁻⁶ m³
Density (ρ) = ?
Calculate density
ρ = m/V
ρ = 60 × 10⁻³/(4 × 10⁻⁶)
ρ = 15 × 10³ kg/m³
6.4. A block of density 8 x 103 kg m-3 has a volume of 60 cm3. Find its mass.
Solution:
Density (ρ) = 8 × 10³ kg/m³
Volume (V) = 60 cm³
V = 60 × 10⁻⁶ m³
Mass (m) = ?
Using formula,
ρ = m/V
and m = ρV
m = 8 × 10³ × 60 × 10⁻⁶
m = 0.48 kg
6.5. A brick measures 5 cm × 10 cm × 20 cm. If its mass is 5 kg, calculate the maximum and minimum pressure which the brick can exert on a horizontal surface.
Solution:
Step 1: Calculate area for each orientation
Minimum area (A1) = 5 cm × 10 cm
A1 = 50 cm² = 5 × 10⁻³ m²
Maximum area (A2) = 10 cm × 20 cm
A2 = 200 cm² = 20 × 10⁻³ m²
Maximum Pressure (P1) = ?
Minimum Pressure (P2) = ?
Step 2: Calculate pressure
P = F/A = mg/A
Force = mg
F = 5 × 9.81
F = 49.05 N
Maximum pressure (P1) = 49.05/(5 × 10⁻³)
P1 = 9,810 Pa
P1 ≈ 1 × 10⁴ Pa
Minimum pressure (P2) = 49.05/(20 × 10⁻³)
P2 = 2,452.5 Pa
P2 ≈ 25 × 10² Pa
6.6. What will be the height of the column in barometer at sea level if mercury is replaced by water of density 1000 kg m-3, where density of mercury is 13.6 × 103 kg m-3
Solution:
Density of water (ρ1) = 1000 kg m-3
Density of mercury (ρ2) = 13.6 × 103 kg m-3
Height of mercury barometer (h1) = 1000 kg m-3
Height of water in barometer (h2) = 1000 kg m-3
Use the pressure equality principle
ρ₁gh₁ = ρ₂gh₂
h₂ = (ρ₁h₁)/ρ₂
h₂ = (13.6 × 10³ × 0.76)/(1000)
h₂ = 10.336 m
h₂ ≈ 10.3 m
6.7. Suppose in the hydraulic brake system of a car, the force exerted normally on its piston of cross-sectional area of 5 cm² is 500 N. What will be the pressure transferred to the brake oil? What will be the force on the second piston of area of cross-section 20 cm2?
Solution:
Force (F1) = 500 N
Area (A1) = 5 cm² = 5 × 10⁻⁴ m
Area (A2) = 20 cm2 = 2 × 10⁻⁴ m
Force (F2) = ?
Calculate pressure in the brake oil
P = F₁/A₁
P = 500/(5 × 10⁻⁴)
P = 1.0 × 10⁶ N/m²
Using Pascal’s law
F₂ = P × A₂
F₂ = (1.0 × 10⁶) × (20 × 10⁻⁴)
F₂ = 2000 N
6.8 Find the water pressure on a deep-sea diver at a depth of 10 m, where the density of sea water is 1030 kg m-3.
Solution:
ρ = 1030 kg/m³
g = 9.81 m/s²
h = 10 m
P = ?
Calculate pressure
P = ρgh
P = 1030 × 9.81 × 10
P = 101,043 N/m²
P ≈ 1.03 × 10⁵ N/m²
6.9. The area of cross-section of the small and large pistons of a hydraulic press is respectively 10 cm2 and 100 cm². What force should be exerted on the small piston in order to lift a car of weight 4000 N?
Solution:
A1 = 10 cm2
A2 = 100 cm2
F1 = ?
F2 = 4000 N
Use Pascal’s law and principle of pressure equality
P₁ = P₂
F₁/A₁ = F₂/A₂
Rearrange to find F₁
F₁ = (F₂ × A₁)/A₂
F₁ = (4000 × 10)/(100)
F₁ = 400 N
6.10. In a hot air balloon, the following data was recorded. Draw a graph between the altitude and pressure and find out:
(a) What would the air pressure have been at sea level?
(b)At what height the air pressure would have been 90 kPa?
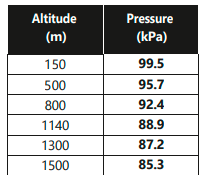
Solution:
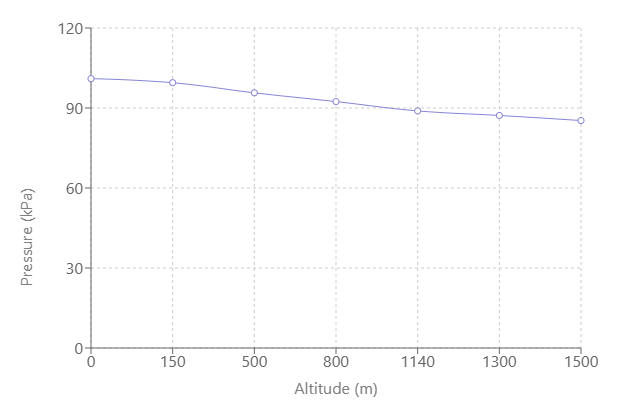
From the graph analysis:
a) By extrapolating the line to sea level (0 m):
Pressure at sea level ≈ 101 kPa
P = 1.01 × 10⁵ Pa
b) For pressure = 90 kPa:
Reading from the graph where the pressure line crosses 90 kPa:
Height ≈ 1.02 km
6.11. If the pressure in a hydraulic press is increased by an additional 10 N cm-2, how much extra load will the output platform support if its cross-sectional area is 50 cm2 ?
Solution:
Calculate pressure from additional force
Area (A1) = 10 cm² = 10 × 10⁻⁴ m2
Area (A2) = 50 cm² =50 × 10⁻⁴ m2
Force (F1) = 10N
Force (F2) = ?
Use Pascal’s law
P = F1/A
P = 10/(10 × 10⁻⁴) = 10⁴ Pa
Calculate force on output platform
F₂ = P × A₂
F₂ = 10⁴ × (50 × 10⁻⁴)
F₂ = 500 N
6.12. The force exerted normally on the hydraulic brake system of a car, with its piston of cross sectional area 5 cm2 is 500 N. What will be the:
(a) pressure transferred to the brake oil?
(b) force on the brake piston of area of cross section 20 cm2?
Solution:
Area (A1) = 5 cm2 = 5 × 10⁻⁴ m2
Area (A2) = 20 cm2 = 2 0× 10⁻⁴ m2
Force (F1) = 500 N
Pressure (P) = ?
Force (F2) = ?
a) Calculate pressure in brake oil:
P = F/A
P = 500/(5 × 10⁻⁴)
P = 1.0 × 10⁶ N/m²
b) Calculate force on second piston:
F₂ = P × A₂
F₂ = (1.0 × 10⁶) × (20 × 10⁻⁴)
F₂ = 2000 N
Class 9 Physics Full Book Numerical Problems with Solution