Physics 1st Year Chapter 5 MCQs are up-to-date and are beneficial for both entry tests and board examinations. Students must prepare these again and again to have the best possible result.
Physics 1st Year Chapter 5 MCQs
FSc 1st Year Physics Chapter 5 MCQs Notes are a helping material for all kinds of papers.
Physics 1st Year Chapter 5 Circular Motion
1 revolution:
One radian is equal to degree:
The SI unit of angular momentum is Js. It can also be expressed as:
The rate of change of angular displacement is called:
Revolution/minute is the unit for:
Time rate of change of angular velocity is called:
The angular acceleration is produced by:
A particle is moving in a circle with constant speed. The direction of centripetal force will be:
Moment of inertia is equal to:
Moment of inertia is measured in:
The angular momentum is given by:
The period of a circular motion is given by:
The direction of linear velocity of body moving in a circle is:
The circumference subtends an angle:
The relation between linear and angular acceleration is:
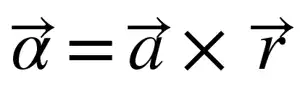
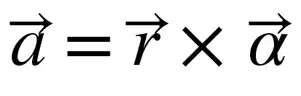
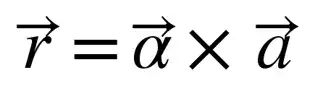
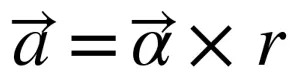
When a body is whirled in a horizontal circle by means of a string the centripetal force is supplied by:
Centripetal force performs work:
When a body moves in a circle of radius „r‟ with linear speed „V‟, its centripetal force is:
The angular acceleration of a body is directed:
The magnitude of the centripetal force on a mass m moving with angular speed 𝜔 in a circle of radius r is:
The dimension of angular acceleration is:
A gymnast sitting on stool with his arms out stretched lowers his arms:
When torque acting on a system is zero, which of the following will be constant:
The rotational K.E of any hoop of radius “r” is given by:
Unit of angular velocity in SI unit is:
Angular speed of daily rotation of earth is:
The rotational K.E of a body is given by:
The minimum velocity necessary to put a satellite into orbit is:
The apparent weight of a man in an ascending lift moving with acceleration “a”:
The apparent weight of a man in a lift moving down with an acceleration of 9.8 𝑚 𝑠^−2 is:
Which electromagnetic wave are used as medium in satellite communication system:
The minimum number of communication satellites required to cover the whole earth is:
The critical speed of an artificial satellite is:
Geo-stationary satellite completes one rotation around earth in:
In case planets the necessary acceleration is provided by:
The acceleration of a freely falling body is:
A man of weight W is standing on an elevator which is ascending with an acceleration a. The apparent weight of the man is:
If a body of mass 10 kg is allowed to fall freely, its weight becomes:
Pull of earth on a mass of 20 kg on the surface of the earth is:
Physics 1st Year Chapter 5 Circular Motion
You got {{userScore}} out of {{maxScore}} correct
{{title}}
{{image}}
{{content}}
Solve More Chapters’ MCQs Online




